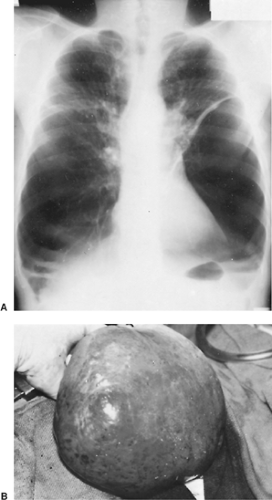
Bilateral bullae though asymmetric disease or even unilateral disease is not uncommon.
Bilateral emphysematous lung fields.
Large holes in the lungs.
A collapsed lung is an uncommon but serious condition that can be life threatening for people in advanced stages of emphysema.
Hyperinflated lungs can be caused by blockages in the air passages or by air sacs that are less elastic which interferes with the expulsion of air from the lungs.
Right middle lobe heard in right axilla.
The presence of mild symptoms is indicative of a progressive condition that has no cure.
Therefore treatment is centered on symptom management.
Paraseptal emphysema refers to inflammation and tissue damage to the distal airways and alveolar sacs near the outer boundaries of the lungs.
Emphysema is a lung condition that causes shortness of breath.
It is not our intention to serve as a substitute for medical advice and any content posted should not be used for medical advice diagnosis or treatment.
Although this condition commonly occurs in the tissue of the neck or chest wall it can develop in.
Basilar predominant disease may be associated with alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency or iv drug use.
Lingula in left axilla.
It measures how much air you can blow out of your lungs in 1 second.
Holes in the lungs known as bullae can.
Apical predominant bullae which are most commonly associated with emphysema in the surrounding lung parenchyma.
Is there any way to determine cause of reduction in lung function.
This reduces the surface area of the lungs and in turn the amount of oxygen that.
Hyperinflated lungs are often seen in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease copd a disorder that includes emphysema.
Over time the inner walls of the air sacs weaken and rupture creating larger air spaces instead of many small ones.
Lower lobes occupy the bottom 3 4 of the posterior fields.
This is a set of guidelines established by the global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease gold.
Doctors call this.
While more common types of emphysema impair major airway structures and disrupt normal airflow paraseptal emphysema is unlikely to cause noticeable breathing problems in its initial stages.
While we encourage individuals to share their personal experiences.
Where in the lungs does emphysema show up.
Upper lobes in the anterior chest and at the top 1 4 of the posterior fields.
In people with emphysema the air sacs in the lungs alveoli are damaged.